Coaxial cables are the unsung heroes of modern communication systems, transmitting high-frequency signals with precision across industries like telecommunications, aerospace, and medical technology. At Petra Carbon, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance coaxial cables designed to minimize signal loss, resist interference, and withstand harsh environments. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive into coaxial cable construction, types, applications, and best practices for integration.
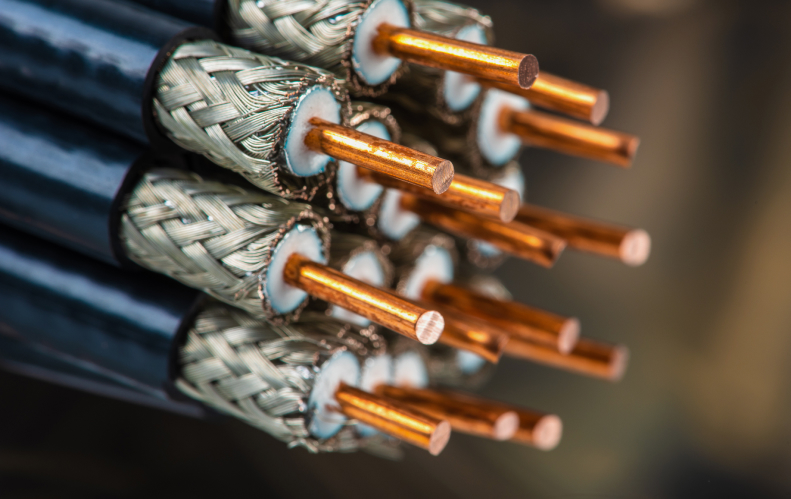

What Is a Coaxial Cable?
A coaxial cable (or “coax”) is an electrical cable with an inner conductor, dielectric insulator, metallic shield, and outer jacket. This layered design ensures signal integrity by preventing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and power loss.
Key Components:
- Inner Conductor: Typically copper or aluminum for conductivity.
- Dielectric Insulator: Separates the conductor and shield (e.g., foam PE, PTFE).
- Metallic Shield: Braided or foil layer to block EMI.
- Outer Jacket: PVC or LSZH materials for durability and fire resistance.
Explore our coaxial cable product range for industry-specific solutions.
Types of Coaxial Cables
Flexible Coaxial Cables
- Ideal for dynamic applications like robotics or test equipment.
- Features braided shields for repeated bending.
- Example: RG-174 (used in GPS and Wi-Fi systems).
Semi-Rigid Coaxial Cables
- Solid outer sheath for fixed installations (e.g., aerospace, base stations).
- Superior shielding for frequencies up to 40 GHz.
- Example: RG-400 (military and avionics).
Triaxial Cables
- Adds a second shield layer for ultra-low noise in medical imaging or sensitive measurements.
Pair these with our RF connectors for end-to-end signal reliability.
Applications of Coaxial Cables
Telecommunications
Backbone of 5G networks, transmitting signals between antennas and base stations.
Pro Tip: Use RF combiners to optimize signal distribution.
Broadcasting
- Delivers HD video/audio signals in broadcast studios and satellite TV systems.
Medical Imaging
- Ensures noise-free data transfer in MRI machines and ultrasound systems.
Industrial Automation
Connects sensors and PLCs in environments with high EMI (e.g., factories using hydraulic pumps).
How to Choose the Right Coaxial Cable
Step 1: Determine Frequency Range
- Low Frequency (≤1 GHz): RG-6 (CCTV, broadband).
- High Frequency (≥10 GHz): RG-402 (radar, aerospace).
Step 2: Assess Environmental Factors
- Temperature: PTFE jackets for extreme heat/cold.
- Flexibility: Braided shields for moving parts.
Step 3: Match Impedance
Most systems use 50Ω (RF) or 75Ω (video).
For custom requirements, contact our team for tailored solutions.
Why Petra Carbon’s Coaxial Cables Excel
Low Signal Loss: Precision-engineered dielectrics for minimal attenuation.
Durability: UV-resistant and flame-retardant jackets for harsh environments.
Compatibility: Tested with Teradyne and Keysight systems.
FAQs About Coaxial Cables
What’s the difference between RG-58 and RG-59?
RG-58 (50Ω) is for RF signals, while RG-59 (75Ω) is for video/CCTV.
Can I repair a damaged coaxial cable?
Temporary fixes are possible, but replacement is recommended. Use in-circuit test systems to diagnose faults.
How long can a coaxial cable run be without signal loss?
Depends on frequency and cable type—use our signal loss calculator to plan installations.
At Petra Carbon, we deliver cables built for reliability, whether you’re designing a 5G network or a medical device.
🔗 Contact Petra Carbon for technical support or browse our Coaxial Cable Catalog.
Stay precise, stay safe!